Buying LEAP Options: A Deep Dive into the Thought Process
This article outlines the process of buying a LEAP (Long-Term Equity Anticipation Securities) option on AMD (Advanced Micro Devices), sharing the thought process behind the decision-making. This provides insights into risk management, technical analysis, and strategic considerations.
Analyzing the Opportunity
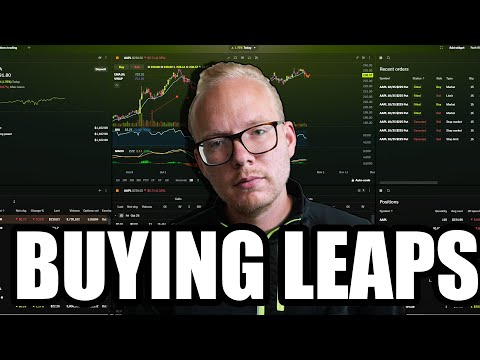
The decision to buy LEAP options on AMD was driven by several factors. First, AMD experienced a significant drop after earnings, presenting a potential buying opportunity.
-
Post-Earnings Dip: AMD's stock price dropped approximately 10% following an earnings announcement.
-
Significant Price Decline: The stock had fallen roughly 34% from its peak to its current trough. This substantial dip was considered a chance to leverage the portfolio.
-
Implied Volatility: Historical implied volatility was relatively low, indicating a favorable environment for buying options.
Portfolio Allocation and Risk Management
Before initiating the trade, a careful assessment of portfolio allocation was conducted to ensure appropriate risk management.
-
Current Allocation: The existing allocation to LEAP options was approximately 6.4% of the total portfolio value.
-
Available Capital: While some capital was previously allocated for swing trading, a decision was made to prioritize LEAP options due to their long-term investment potential.
-
Selling Existing Shares: To free up capital for the LEAP option purchase, a portion of existing AMD shares were sold.
Option Chain Analysis
The process of selecting the appropriate LEAP option involved a detailed analysis of the option chain.
-
Expiration Date: An expiration date approximately one and a half years out was chosen. The reasoning being going too far out locks up money in time value that could be used elsewhere.
-
Strike Price: The 100 strike price was selected.
-
Key Metrics Considered:
-
Volume and Open Interest: High volume and open interest indicate greater liquidity.
-
Delta: A Delta between 0.75 and 0.90 was preferred, balancing risk and potential reward.
-
Bid-Ask Spread: The bid-ask spread was evaluated as a percentage of the option's value to assess liquidity.
-
Executing the Trade
The execution of the trade involved careful negotiation to obtain a favorable price.
-
Selling Shares: AMD shares were sold at market price to generate the necessary capital.
-
Negotiating the Option Price: An attempt was made to negotiate a price in the middle of the bid-ask spread, resulting in cost savings.
Post-Trade Analysis
After the trade was executed, the performance was immediately assessed.
-
Fill Quality: The initial performance of the option was evaluated to determine if a good fill price was obtained. A small initial loss was considered acceptable, indicating a reasonable fill.
-
Revised Portfolio Allocation: Following the trade, the portfolio allocation to LEAP options increased to approximately 8%.
Additional Considerations
-
Liquidity: While current liquidity was deemed acceptable, it was acknowledged that liquidity typically improves as the expiration date approaches.
-
Rolling Options: The possibility of rolling the option closer to the expiration date was considered as a strategy to manage time decay and maintain leverage.
-
Exercising Options: In situations where liquidity dries up, exercising the option was identified as a viable alternative.
Final Thoughts
The overall strategy involved buying the dip on AMD after a significant price decline, leveraging LEAP options to amplify potential gains. Risk management was a key consideration throughout the process, with careful attention paid to portfolio allocation and option selection.
 {#
{#  {#
{#  {#
{#  {#
{#  {#
{#